Did you know that having an above-average waist circumference can put you in the ‘high-risk’ category for heart diseases?
Or that physical inactivity is independently responsible for approximately 12.2% of heart attacks (medical term: myocardial infarction)?
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the leading causes of high blood cholesterol, increased visceral fat, and decreased cardiac endurance. It increases the risk for diabetes and obesity, which, in turn, increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Cardiovascular: it’s the system of heart and blood vessels. ‘Vascular’ refers to the blood vessels – arteries and veins – in your body. ‘Cardio’ refers to the heart.
Ideally, we need to focus on primary prevention and work on eliminating the root causes of diseases by encouraging exercise, getting rid of inactive habits, and promoting a culture of a healthy diet.
But primary prevention isn’t given the attention it deserves.
Most people consider exercising and changing their inactive lifestyles only after their physician tells them that they’re at risk for cardiac issues.
Still, it’s better to start late than never.
In this article, we’ll talk about why you need to consult a cardiovascular physiotherapist to help you prevent cardiac diseases, either before or after you develop risk factors.
We’ll also show you all the various ways in which physical therapy improves your cardiac health and decreases the risk for heart problems.
What Is Involved in Cardiovascular Physiotherapy?
Cardiovascular physiotherapy includes education, activity modifications, and exercise sessions 3-4 times a week under the supervision of a qualified PT.
Cardiovascular Physiotherapy programs are designed to increase your quality of life, halt disease progression, reduce secondary complications due to risk factors and decrease mortality due to CVDs through exercises and lifestyle modifications.
The participants of such a program are usually people recovering from a heart attack or coronary artery bypass surgery. So the programs are often aimed at rehabilitation.
But these are just as effective as prehab to prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Why Do You Need Cardiovascular Physical Therapy for the Prevention of Cardiac Diseases?
Often when you’re diagnosed with a heart or vascular problem, you’re prescribed medications to manage that and asked to come for regular checkups.
While some medication is necessary, relying only on bottles of pills and taking a ton of prescription medications every day isn’t the best way to manage cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) or their risk factors.
Increasing physical activity, exercising properly and managing diet are some effective ways of dealing with cardiac issues that are usually ignored.
Most people believe that they can go to the gym, increase their exercise level, and manage their heart condition by themselves with no medical knowledge.
And many actually do exactly that when they find out that they’re at risk for a heart attack or something similar.
But that can be dangerous because you might not know the level of physical activity that’s safe for your heart.
Research shows that suddenly and drastically increasing your activity increases thrombin formation and platelet adhesiveness in certain conditions in inactive adults. (Reference) In simple terms, it increases your chances of developing a blood clot.
That’s not a major issue if you’re healthy, but if you’re already at risk for heart problems then this could be dangerous.
You need physiotherapists to guide you on which exercises you must do, how much activity is okay, and when you’re ready to progress to more intense exercises.
They keep an eye on your heart rate, SpO2 levels, blood pressure, and exertion level while exercising which helps them know how you’re performing so they don’t overwork you.
Some cardiac conditions can cause your blood pressure to rise and fall suddenly. Physiotherapists are educated on all the details of different diseases, so they help you follow the precautions related to your condition.
Hence, you should work with physios so you can safely increase your physical activity and reap the maximum benefits from it.
Which are the Most Common Cardiovascular Diseases?
Some commonly occurring cardiovascular diseases include:
1. Atherosclerosis
This is the accumulation of plaques inside your blood vessels. These plaques are made of fatty components which can break away anytime and form a clot in the blood vessels.
If an artery of the heart gets blocked due to excessive fatty deposits or a blood clot, it can cause a heart attack.
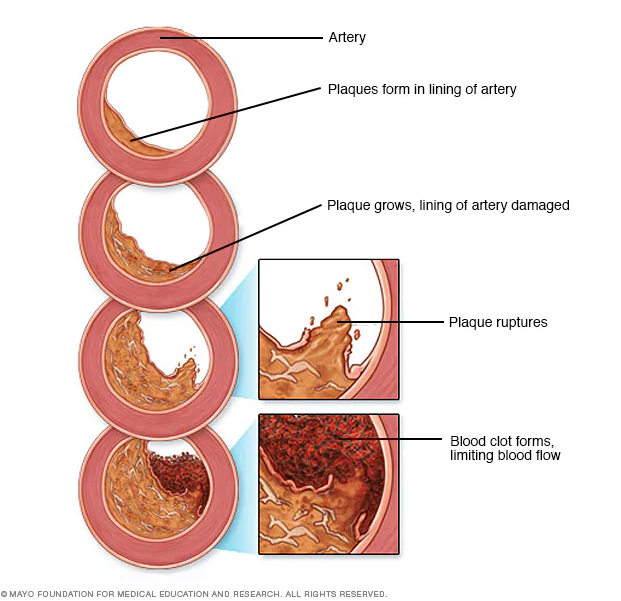
2. Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
It’s also known as coronary artery disease. It’s a condition where the blood flow to the heart muscles is reduced.
That leads to oxygen deprivation and chest pain. If the blood supply isn’t restored, it can cause a heart attack or heart failure.
3. Stroke
It’s a condition where a portion of the brain is deprived of blood. The supply is cut off due to a blood clot or because of a ruptured blood vessel.
This falls under the ‘vascular’ component of cardiovascular diseases.
It can cause brain damage, paralysis, and death.
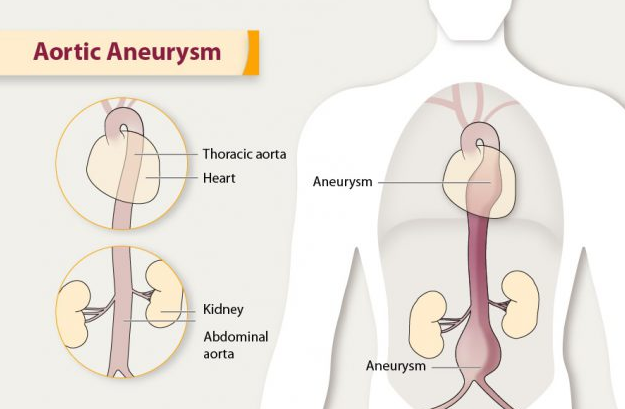
4. Aortic Aneurysm
The Aorta is the largest blood vessel in your body and it’s responsible for transporting the blood out of the heart and into the body.
An aortic aneurysm is a condition when this vessel becomes weak and bulges outwards like a tiny balloon.
It can be life-threatening if it bursts.
5. Chronic Heart Failure
It’s a condition where the heart can’t pump enough blood to keep the rest of the body functioning properly.
This usually happens as a secondary condition due to other heart problems such as rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy (problem with the muscles of the heart) or ischemic heart disease (injury due to a lack of oxygen to the heart).
It’s called ‘chronic’ when this condition persists for longer than 3 months.
Most heart problems have similar symptoms including chest pain, difficulty breathing, lightheadedness, cold sweats, and sometimes vomiting.
How Do You Know If You’re at Risk for Heart Problems?
People who’re overweight, regular smokers, and physically inactive are at risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Some other risk factors for CVDs include:
- An unhealthy diet that’s high in cholesterol
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Family history of heart problems
- Old age (above 40)
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Bad socioeconomic conditions
You can know if you’re at risk for heart problems by going to your doctor and getting tests done. Your GP will take your history and tell you about your lifestyle habits that might be negatively affecting your heart and vascular system and review your test reports to see how much damage is already done.
If your doctor has told you about any of these risk factors, it’s wise to come to a cardiopulmonary or cardiovascular physical therapy center and get yourself a treatment plan to prevent the heart problems from becoming more serious and decrease the risk of another event.
How Does Physiotherapy Help You Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases?
Physiotherapists are trained professionals who know how to assess the condition of your heart and calculate the amount of load you can manage.
Using the data from various tests, they design exercise programs that improve your cardiac health. Physiotherapy helps to slow the progression of diseases and decrease the danger of risk factors.
Here are some ways that physiotherapy can help you avoid major cardiovascular events if you’re at risk for them:
1. Reliable Advice on Lifestyle Modifications
Recent studies show that if you’re inactive for most of your day and then participate in some moderate to vigorous physical activities for a few minutes or an hour, then it won’t be enough to counter the negative effects of your sedentary lifestyle. (Reference)
A physical therapist can advise you on how to practice low to moderate level activities throughout your day so that you holistically improve your lifestyle and cardiovascular health.
That kind of advice or program is customized. A physio will take your baseline values after performing some tests, then determine how much activity you need and advise you accordingly.
2. Management of Heart Failure
Physical activity has an inverse relationship with heart diseases and cardiac events. Just by walking, you could have a 35% lower risk of coronary events than someone who doesn’t walk as frequently. (Reference)
Plaque formation (medical term: atherosclerosis) in the arteries close to the heart is one of the causes of heart failure.
Exercising regularly modifies the structure of the blood vessels to make them antiatherogenic – that means your arteries become less prone to developing plagues. (Reference)
That reduces the risk of heart failure even if you have other risk factors such as high cholesterol, coronary artery disease and high blood pressure.
3. Strengthen Muscles of the Heart
Regular physical activity puts your heart under good stress that keeps the muscles in excellent shape.
That’s important because the muscles of the heart are responsible for pumping blood into the lungs and the body so these need to be strong – more so if you’re at risk for heart problems.
In case you end up suffering from a cardiac event, good strength of heart muscles reduces the after-effects of heart attack and prevents recurrence.
4. Improve Blood Flow
Performing aerobic exercises increase blood to the heart muscles and all over the body because of improved endothelial function.
It also makes the cardiac muscles more responsive to vasoactive substances which helps the heart perform well under stress by allowing more blood to flow to it. (Reference)
Vasoactive: It’s any substance that affects the diameter of the blood vessels. These either relax or contract the layers of the vessels.
Aerobic physical activity improves the flow of blood from the blood vessels into the heart muscles (term: myocardial perfusion) in patients with coronary artery disease.
That’s why these types of activities are widely used in cardiac rehab and disease prevention programs in cardiovascular physical therapy.
5. Blood Pressure Management
Exercising regularly increases the health of your blood vessels. Inactivity and some of the conditions that put you at risk for cardiac problems can cause your arteries to stiffen due to cholesterol accumulation or other similar issues.
Research shows that being physically active reduces arterial stiffness enough to reduce systolic blood pressure and afterload. (Reference)
Afterload: This is the amount of resistance that heart muscles have to overcome to pump the blood out of the heart. A higher value is associated with hypertension or high blood pressure and a reduced amount of fresh blood in the body.
This is highly beneficial for people at risk for heart attacks. That’s because if they did happen to suffer from one, increased coronary perfusion can prevent the heart muscles from dying (medical term: necrosis) due to a lack of oxygen (medical term: myocardial ischemia).
Some portions of the heart muscles will inevitably suffer but maintaining a good blood supply to the heart can minimize the damage caused by a heart attack.
The Takeaway
You’re never too young to be concerned about heart problems.
Just in the past decade, cardiovascular diseases have been responsible for over 30% of all deaths. That makes it the number one cause of death globally. (Reference)
Out of all the CVD deaths, 85% are due to heart attacks and stroke.
Nearly ¾ of deaths due to cardiovascular events can be prevented with lifestyle modifications. (Reference)
Most patients are unaware of how great physical therapy can be for the health of their heart and blood vessels.
Unless their physician or surgeon tells them to contact a PT, most people after finding out that they’re at risk for a cardiac event just go home and make some changes in their activity levels and diet – however they see fit.
That’s not the safest way to go.
Cardiovascular physical therapy can improve your quality of life if you’re at risk for CVDs.
If you want to improve your cardiac health and avoid becoming another statistic, contact a cardiovascular physiotherapist today and get yourself a proper assessment – and, if need be, enroll in a primary prevention cardiac fitness program.
Disclaimer: This article is for informative purposes only. We provide well-researched and authentic information. Do not consider this personalized health advice. Please contact a licensed healthcare professional for medical issues and health concerns.